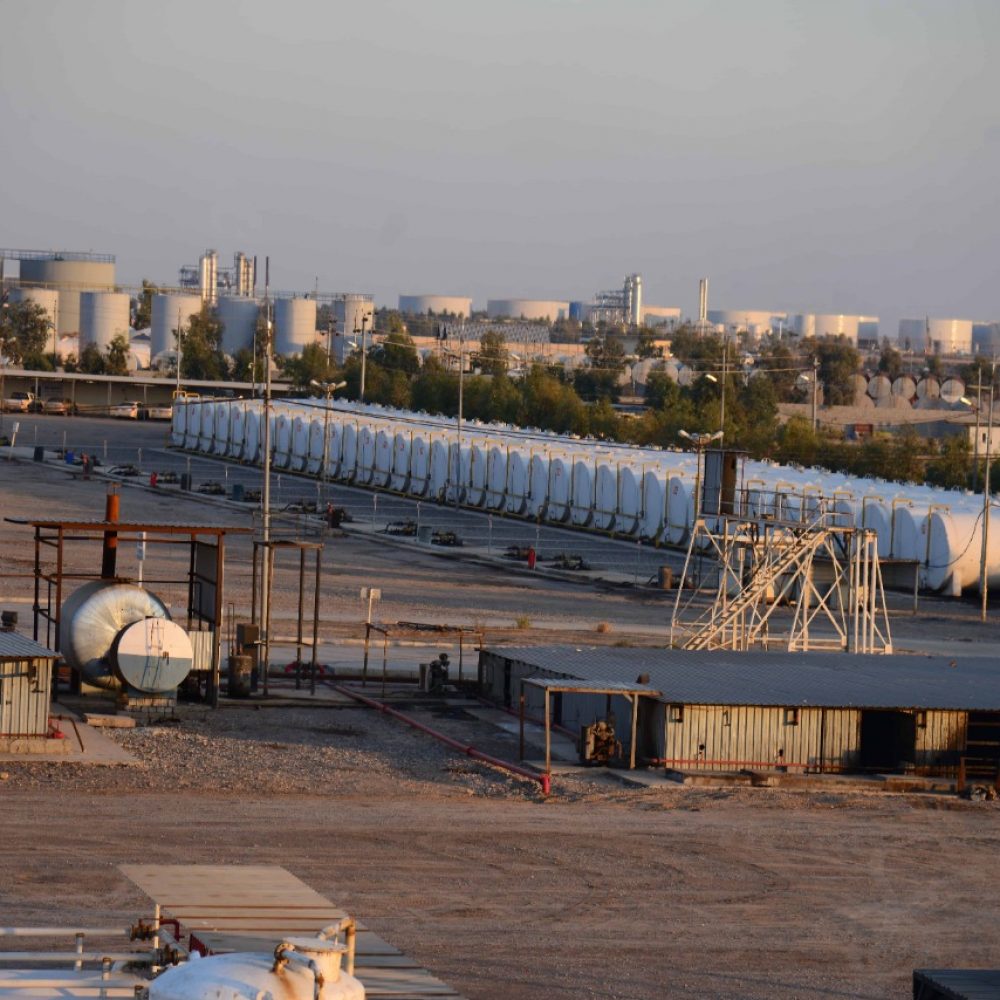
Our company was established to address and to engage in a wholesale and distribution of Petroleum products within the oil industry.
What we do
We strive to maintain highest standards while exceeding client’s expectations at all levels. Please find our services.cross-platform integration. Collaboratively administrate empowered markets via plug-and-play networks.
- Base Oil
- Bitumen
- Gasoline
- liquefied petroleum gas (LPG)
- Fuel Oil
- Naphtha
- Gas Oil
is a derivative product of crude oil/petroleum. It is derived during fractional distillation process and has a translucent liquid form. It’s not used in its crude form.Majorly all around the world gasoline is used as fuel for vehicles. It’s one of the main products, which is consumed heavily worldwide.
BASE OIL
are used to manufacture products including lubricating greases, motor oil and metal processing fluids which are initially produced by means of refining crude oil (mineral base oil) or through chemical synthesis. This means that crude oil is heated in order that various distillates can be separated from one another. During the heating process, light and heavy hydrocarbons are separated – the light ones can be refined to make petrol and other fuels, while the heavier ones are suitable for bitumen and base oils.
Most every lubricant used in plants today started off as just a base oil. The American Petroleum Institute (API) has categorized base oils into five. This breakdown is based on the refining method and the base oil’s properties in terms of, among other things, viscosity, and the proportion of saturates and sulfur content.
Group 1
API defines group I as “base stocks contain less than 90 percent saturates and/or greater than 0.03 percent sulfur and have a viscosity index greater than or equal to 80 and less than 120”.
Group 2
API defines group II as “base stocks contain greater than or equal to 90 percent saturates and less than or equal to 0.03 percent sulfur and have a viscosity index greater than or equal to 80 and less than 120”.
Group 3
API defines group III as “base stocks contain greater than or equal to 90 percent saturates and less than or equal to 0.03 percent sulfur and have a viscosity index greater than or equal to 120”.This group may be described as Synthetic Technology oils or Hydro-Cracked Synthetic oil.
Group 4
base oils have a viscosity index range of 125 – 200.
Group 5
base oils are classified as all other base oils, including silicone, phosphate ester, polyalkylene glycol (PAG), polyolester, biolubes, etc. These base oils are at times mixed with other base stocks to enhance the oil’s properties. An example would be a PAO-based compressor oil that is mixed with a polyolester. Esters are common Group V base oils used in different lubricant formulations to improve the properties of the existing base oil. Ester oils can take more abuse at higher temperatures and will provide superior detergency compared to a PAO synthetic base oil, which in turn increases the hours of use.
is a low-grade of crude oil which is composed of complex, heavy hydrocarbons. In an oil reservoir, bitumen is a thick, viscous fluid and must be extracted from the ground. When extracting it, a lot of heat and effort must be used to upgrade it to a better product. Although bitumen is hard to extract from the ground, it can bubble naturally to the surface of the Earth in petroleum seeps. These seeps are places where fossil fuels and petroleum products leak out of the Earth instead of being trapped deep below the ground. In these seeps, bitumen, asphalt, and tar bubble up into pools. Additionally, bitumen is the main fossil fuel component of oil sands. Bitumen is a beneficial material that is used in various industries. More than 85% of the world’s bitumen production is used for road construction, 10% is used in other constructions and 5% is used in a variety of other industries, including insulation.
liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) any of several liquid mixtures of the volatile hydrocarbons propene, propane, butene, and butane.
Liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) is recovered from “wet” natural gas (gas with condensable heavy petroleum compounds) by absorption. The recovered product has a low boiling point and must be distilled to remove the lighter fractions and then be treated to remove hydrogen sulfide, carbon dioxide, and water.
It is also known as heavy oil, marine fuel, or furnace oil. Fuel oil, which is distilled from crude oil and often left as residue during the refining process, refers to a range of the least volatile and heaviest of the commercially used fuels i.e., heavier than gasoline and naphtha. In general terms, fuel oil is used to burn in a furnace or boiler for the generation of heat or used in an engine for the generation of power.
AccordNaphtha is any of various volatile, highly flammable liquid hydrocarbon mixtures, made from distilled petroleum. It is used chiefly as solvents and diluents to make high octane gas, as raw materials for conversion to gasoline, and cleaning metals. The demand for Naphtha is expected to surpass 6.5 mb/d in 2020.ion Content
A middle distillate and form of heating oil used primarily in internal combustion engines such as vehicles and trucks. One of the most actively traded oil products, gasoil is the underlying in a key International Petroleum contract. In refining terms, gasoil comes between fuel oil and the lighter products such as naphtha and gasoline. In its broader definition, it covers the oil products used for diesel automotive fuel and jet fuel